Programs Near You
Select a program of interest down below and we'll connect you with schools that match
How to Become a Medical Billing and Coding Specialist
Updated October 20, 2025 | Brad Fishbein
- What Do Medical Billing and Coding Specialists Do?
- Salary & Job Outlook
- How to Become a Medical Billing and Coding Specialist (5 Steps)
- Certification & Licensing Requirements
- Skills That Make Great Coders
- Work Environment & Career Options
- Pros & Cons of Medical Coding Careers
- Related Healthcare Careers
- Start Your Medical Coding Journey
Interested in a career in healthcare—without years of medical school?
Becoming a medical billing and coding specialist could be your perfect path. In this 2025 guide, you’ll learn every step—from accredited training to certification and job placement.
If you’re detail-oriented, tech-savvy, and enjoy organizing information, this growing healthcare field offers strong pay, remote flexibility, and job security.
Medical coders and billers translate medical procedures into standardized codes used for insurance claims and healthcare records. Their work keeps hospitals, clinics, and doctors’ offices running efficiently.
What Do Medical Billing and Coding Specialists Do?
Medical coders and billers work behind the scenes of healthcare—turning patient information into standardized data that drives treatment records, billing, and insurance reimbursement.
Typical Duties Include:
- Reviewing patient charts and clinical documentation
- Assigning ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS medical codes
- Preparing and submitting insurance claims
- Ensuring HIPAA compliance and accurate recordkeeping
- Communicating with providers, patients, and insurance carriers
Many professionals specialize in hospital coding, physician offices, or outpatient care centers. Others work remotely for large healthcare networks.
Salary & Job Outlook
| Quick Facts | Medical Billing & Coding Specialists |
|---|---|
| 2024 Median Pay | $50,250 per year / $24.16 per hour |
| Typical Entry-Level Education | Postsecondary certificate or associate degree |
| Work Experience Required | None |
| Number of Jobs (2023) | 194,800 |
| Job Outlook (2023–33) | 7% growth (Much faster than average) |
| Employment Change (2023–33) | +13,800 jobs |
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics – Medical Records Specialists
As healthcare expands and moves digital, certified coders are in high demand, especially in insurance, telehealth, and hospital systems.
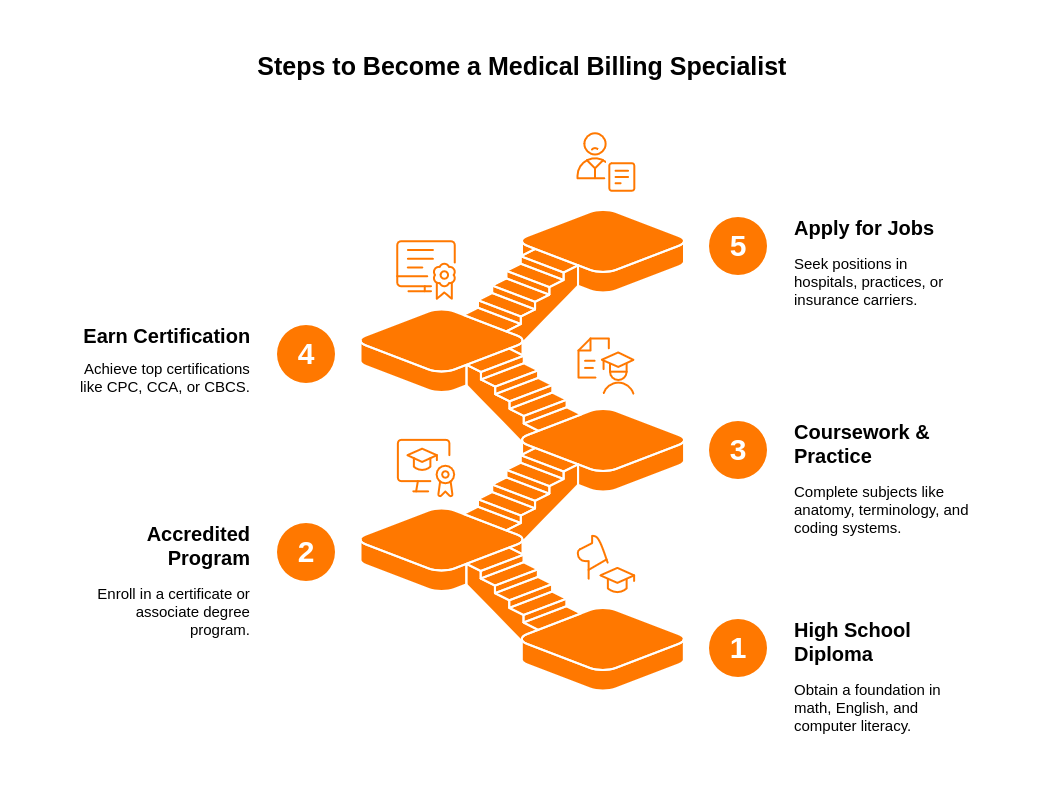
How to Become a Medical Billing and Coding Specialist (5 Steps)
Becoming a certified medical billing and coding professional typically takes 9–24 months, depending on your chosen path.
-
Earn your high school diploma or GED
A foundation in math, English, and computer literacy helps in training. -
Enroll in an accredited medical billing & coding program
Choose a certificate or associate degree from an accredited school.
-
Complete coursework & hands-on practice
Subjects include anatomy, medical terminology, coding systems, and insurance regulations. -
Earn certification
Top certifications include:- CPC (Certified Professional Coder) – AAPC
- CCA (Certified Coding Associate) – AHIMA
- CBCS (Certified Billing & Coding Specialist) – NHA
-
Apply for jobs or remote positions
Graduates often work for hospitals, private practices, or insurance carriers.
Certification & Licensing Requirements
While most states don’t require a license, national certification greatly improves job prospects and salary potential.
Major Certifying Organizations:
- AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders) – CPC, CPB, CPMA
- AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association) – CCA, CCS, RHIT
- NHA (National Healthcareer Association) – CBCS
Most employers prefer certified candidates, and some healthcare systems reimburse exam fees once you’re hired.
Skills That Make Great Coders
- Strong attention to detail and accuracy
- Analytical and problem-solving skills
- Understanding of medical terminology and anatomy
- Computer proficiency and EHR familiarity
- Discretion with confidential patient data
If you enjoy precision work, organization, and the healthcare field—this is a career where those strengths shine.
Work Environment & Career Options
Medical billing and coding specialists work in:
- Hospitals and clinics
- Private practices
- Insurance companies
- Remote/home offices
Specializations include:
- Inpatient coding
- Outpatient coding
- Medical auditing
- Billing management
Pros & Cons of Medical Coding Careers
Pros:
- Remote and hybrid job options
- Entry within 1–2 years
- Stable, growing field
- Strong earning potential
Cons:
- Sitting or screen-heavy work
- Repetitive coding tasks
- Certification renewal required
Related Healthcare Careers
- Medical Assistant Careers
- Pharmacy Technician Careers
- Dental Assistant Careers
- Healthcare Administration Careers
Start Your Medical Coding Journey
Medical billing and coding offers a fast, flexible route into healthcare—without patient care duties or long degrees.
Whether you want to work in a hospital, private office, or from home, training programs can help you launch your career in under two years.
You can code the future of healthcare—one claim at a time.
Explore Related Topics:
Notice an update we should make?
We strive for accuracy. Contact us here if you see incorrect or outdated info on this page.

Meet the author: Brad Fishbein is a Florida Licensed Mold Assessor and council-certified Microbial Investigator. He’s the founder of TradeCareerPath.com and has completed over 5,000 mold inspections since 2009. Brad now helps homeowners and tradespeople make smart decisions about mold, licensing, and skilled career paths.
.svg)