Programs Near You
Select a program of interest down below and we'll connect you with schools that match
How to Become an Auto Mechanic
Updated August 1, 2025 | Brad Fishbein
Want to become an auto mechanic? Most people get started through a trade school or hands-on apprenticeship, often becoming certified within 1–2 years. This guide breaks down every step—from training and ASE exams to career options and pay.
If you love solving problems, working with your hands, and bringing engines back to life—you’re in the right trade.
Auto mechanics are the backbone of transportation. From EVs to diesel fleets, skilled technicians are more in demand than ever as vehicle technology keeps evolving.
Auto Mechanic Salary Snapshot
U.S.70,000 openings/yr
What Does an Auto Mechanic Do?
Auto mechanics inspect, repair, and maintain vehicles of all types—cars, trucks, SUVs, and even hybrids or electric models. Depending on specialization, they might:
- Diagnose engine and electrical issues
- Replace worn parts (brakes, suspension, transmission)
- Use computerized diagnostic tools
- Perform routine maintenance and inspections
- Work in dealerships, shops, or fleet service centers
Some even go on to specialize in EV technology, performance tuning, or diesel mechanics.
Auto Mechanic Salary & Job Outlook
Based on BLS occupation: Automotive Service Technicians and Mechanics (49-3023)
Data Year: 2024 • U.S.
Mean Pay (2024)
Wage Percentiles
Employment Outlook
Employment: 805,600 → 839,200 jobs by 2034 (4.2%)
70,000 projected openings each year
Additional Details
- Share of U.S. Employment
- 0.4%
- Employment per 1,000 Jobs
- 4.47
- Employment RSE
- 0.6%
- Projected Annual Openings
- 70,000
Tip: ASE-certified mechanics and those skilled in hybrid or EV systems often earn significantly more.
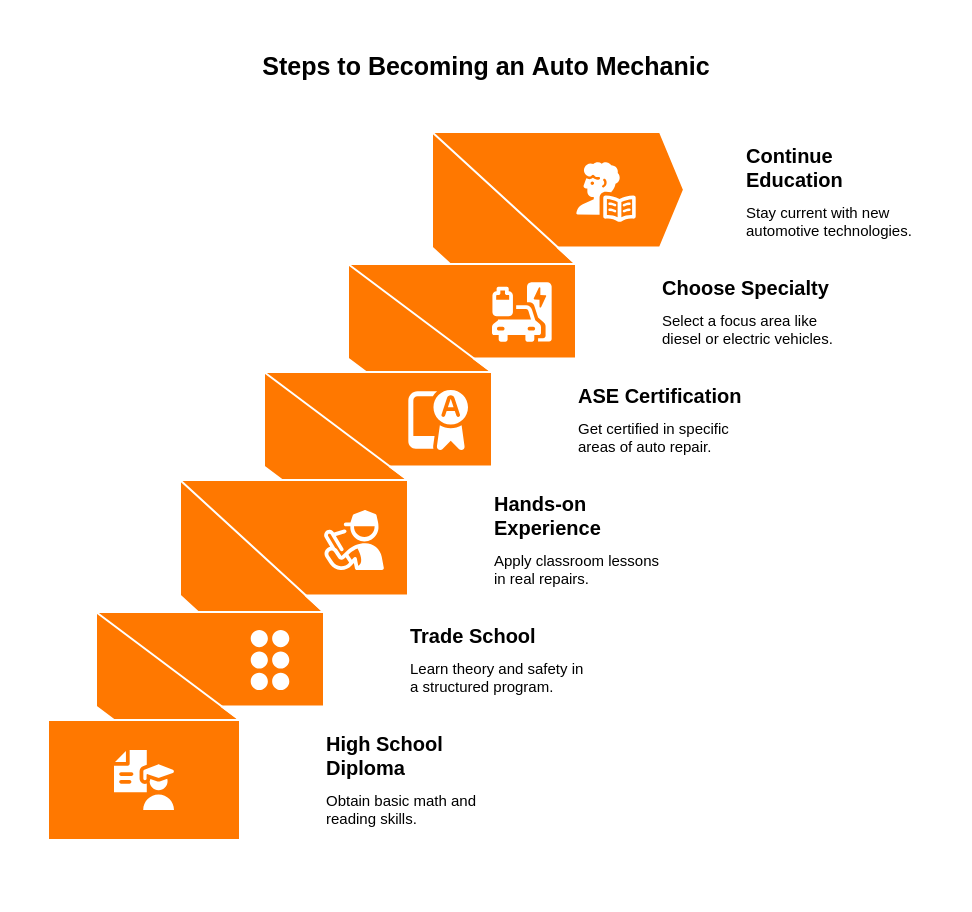
How to Become an Auto Mechanic (6 Steps)
Becoming a mechanic is straightforward, but requires skill, patience, and hands-on learning.
-
Earn a high school diploma or GED
You’ll need basic math and reading skills for diagnostics and manuals. -
Enroll in an auto mechanic trade school
Learn theory, safety, and engine systems in a structured program.
Auto Mechanic Training Programs
-
Get hands-on experience
Apprenticeships or entry-level shop work help you apply classroom lessons in real repairs. -
Earn ASE Certification
The National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) certifies mechanics in areas like brakes, suspension, or hybrid systems. -
Find your specialty
Choose between general auto repair, performance, diesel, or electric vehicles. -
Continue education
Automotive tech changes fast—stay current with new models and systems.
Where to Get Certified
While ASE certification is national, some states require additional licensing or registration for emissions or inspection work.
| Certification | Details |
|---|---|
| ASE A-Series | Covers 9 main automotive areas including engines, brakes, and transmissions |
| EPA Section 609 | Required to work on air conditioning systems |
| Manufacturer Training | OEM courses (Toyota, Ford, GM, etc.) for dealership techs |
Why Choose Trade School?
Trade schools provide a faster, focused path into the workforce—usually 6 to 18 months.
Advantages:
- Hands-on shop training with modern diagnostic tools
- Structured curriculum and certification prep
- Job placement help after graduation
- Eligible for Pell Grants and GI Bill
Drawbacks:
- Tuition costs (though lower than traditional college)
- Some states still require field hours before full certification
Many mechanics complete trade school first, then move into a shop or dealership while studying for ASE exams.
Explore mechanic programs by state or find local options below:
Skills Every Mechanic Needs
- Mechanical and electrical aptitude
- Attention to detail
- Diagnostic problem-solving
- Communication with customers
- Willingness to stay current with new tech
If you like working with tools, solving puzzles, and helping people get back on the road, you’ll fit right in.
Pros & Cons of the Automotive Trade
Pros:
- Learn a lifelong skill in 1–2 years
- Strong job stability and growth for ASE-certified techs
- High potential for shop ownership or specialization
Cons:
- Physically demanding work
- Some exposure to noise and fumes
- Must keep certifications current
Related Trades to Explore
Start Your Mechanic Career
Whether you want to repair daily drivers or performance cars, skilled auto mechanics will always be in demand.
Find your training program today and start turning your passion for cars into a career.
Explore Related Topics:
Notice an update we should make?
We strive for accuracy. Contact us here if you see incorrect or outdated info on this page.

Meet the author: Brad Fishbein is a Florida Licensed Mold Assessor and council-certified Microbial Investigator. He’s the founder of TradeCareerPath.com and has completed over 5,000 mold inspections since 2009. Brad now helps homeowners and tradespeople make smart decisions about mold, licensing, and skilled career paths.
.svg)